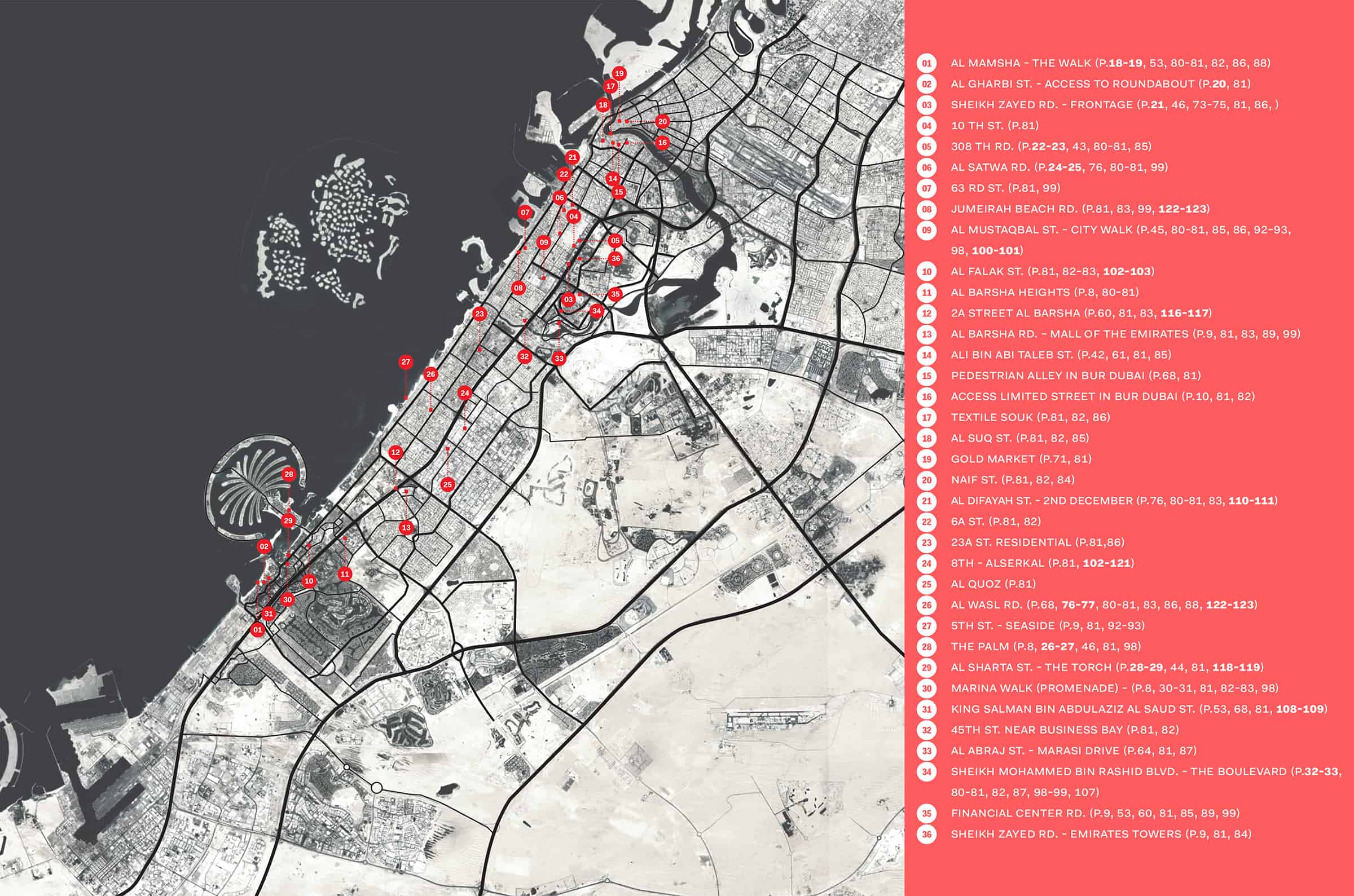
Dubai Street Atlas Walkable Cities of Tomorrow
Street Atlas
“Streets and their sidewalks, the main public places of a city, are its most vital organs. Think of a city and what comes to mind? Its streets.”
– Jane Jacobs
Planning Dubai
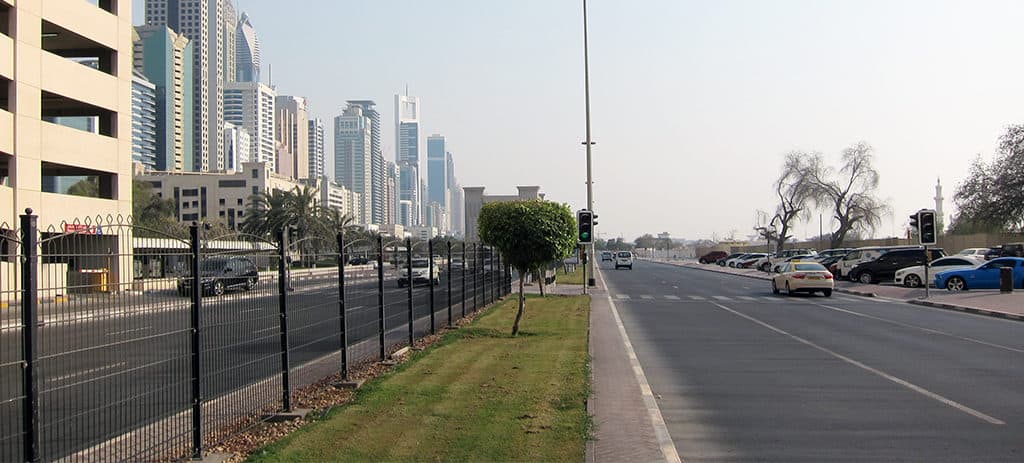
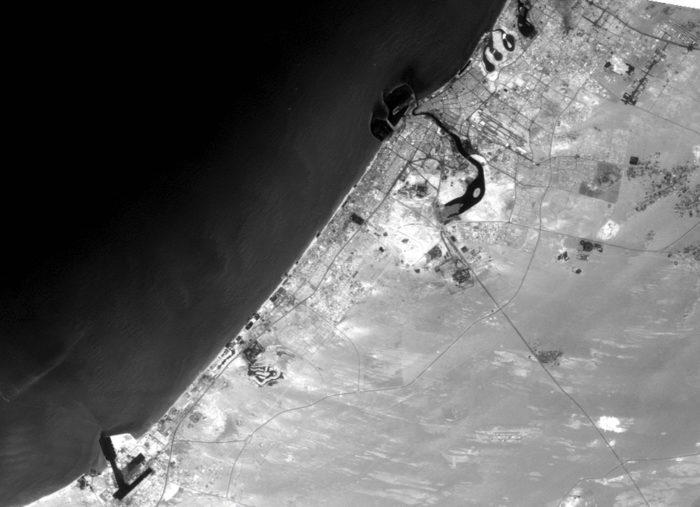
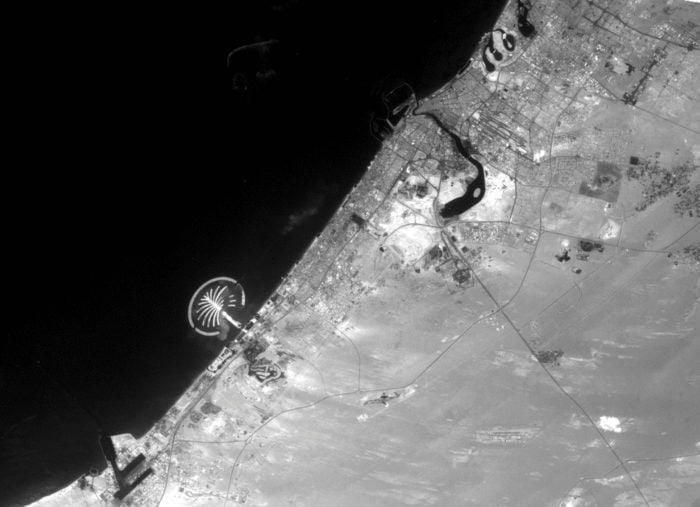
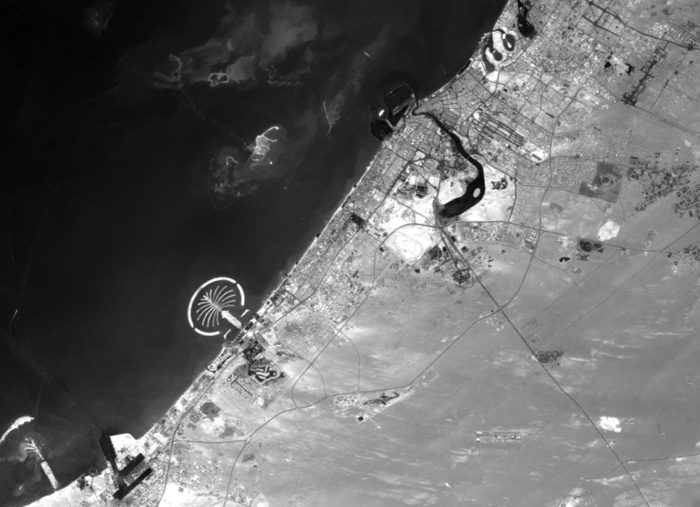
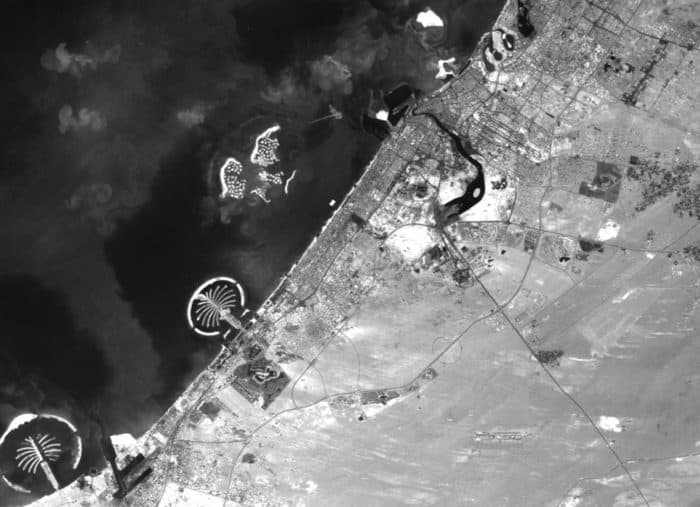
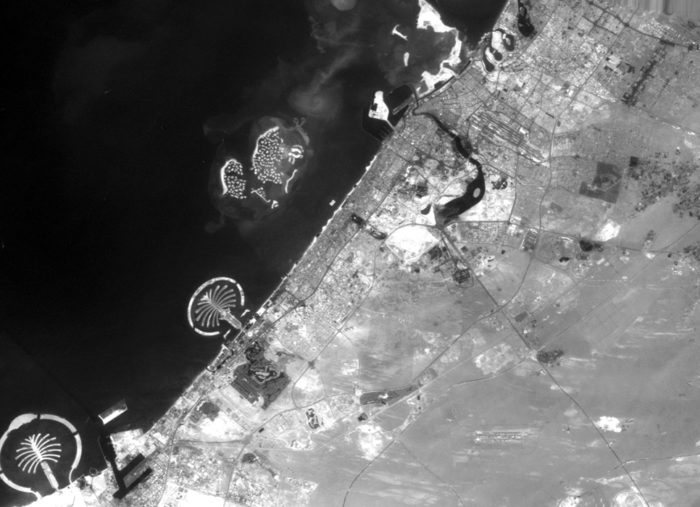
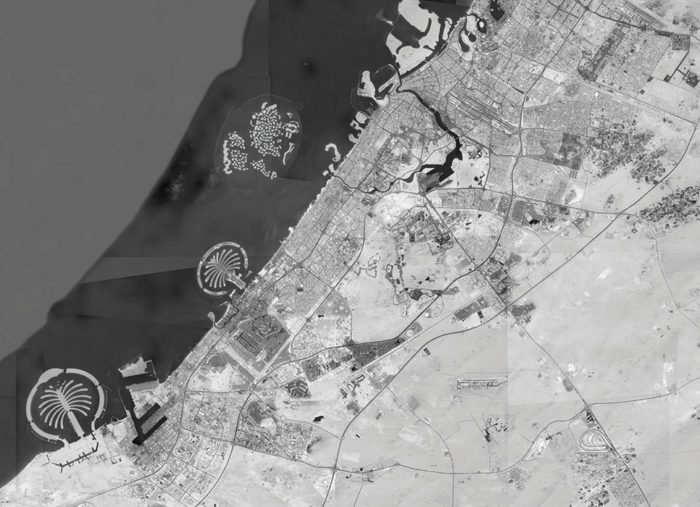
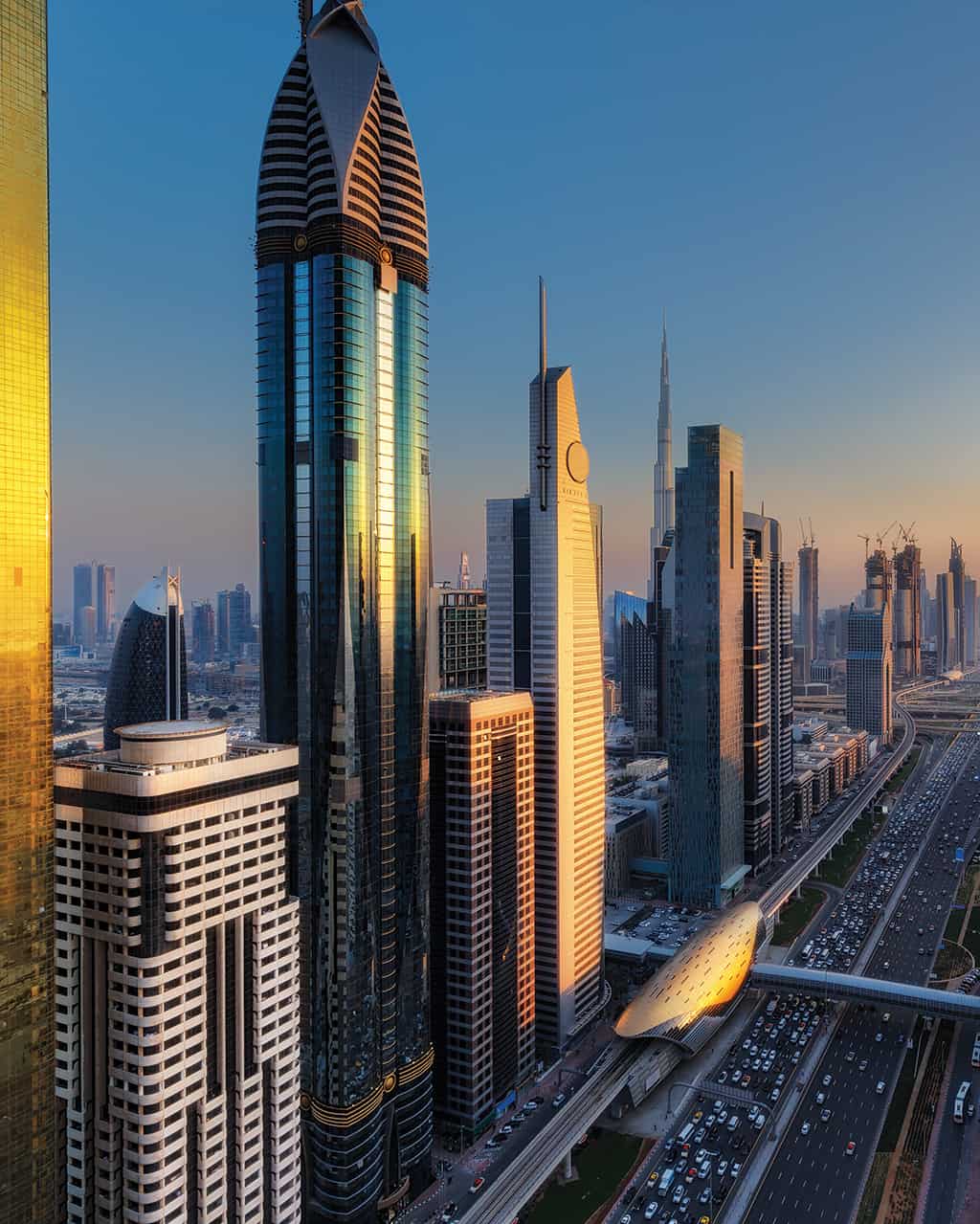
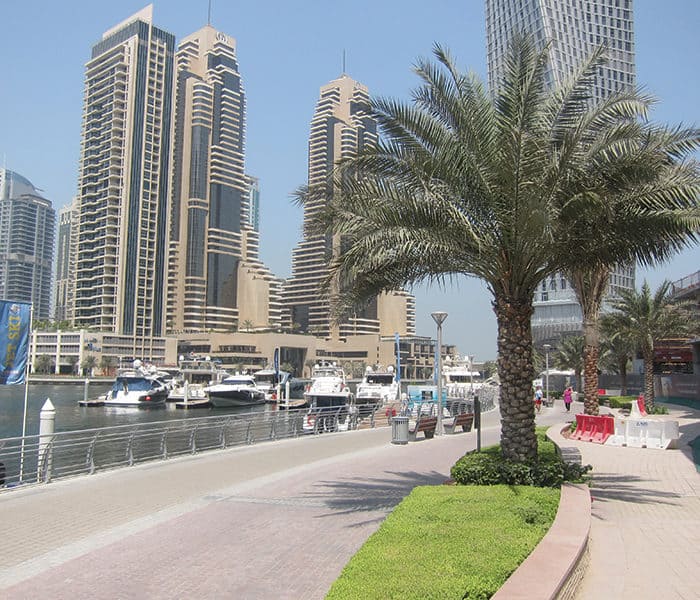
The city has witnessed an exceptionally fast-paced urban growth during the past three decades, hence becoming one of the most iconic cities in the world, well known for its skyscrapers, luxurious resorts and diverse attractions. What about its streets?
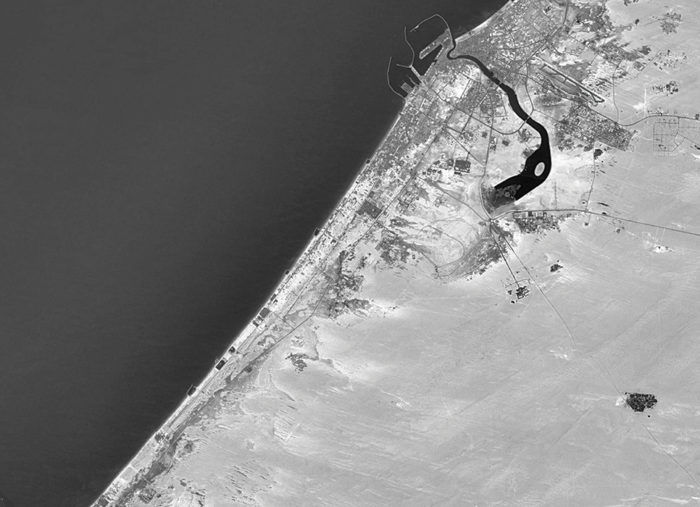
Time lapse – an unprecedented (steady) growth
Dubai’s urban fabric is extended rapidly over 400 times and this resulted in many urban planning challenges especially in terms of urban mobility. Currently moving around the city is facilitated through six-lane highways, flyover junctions, overhead transit rail and a new tramline although as the city will be expanding even more through the coming years and is planning for EXPO 2020, with 25 million expected visitors, it is time to enhance and improve the quality of its urban fabric and public space.
Reading the City
Studying available information and predicting future possibilities are the two key elements defining the planning process. In order to study the current situation of Dubai urban fabric, the following five cutting-edge analytical tools are used:
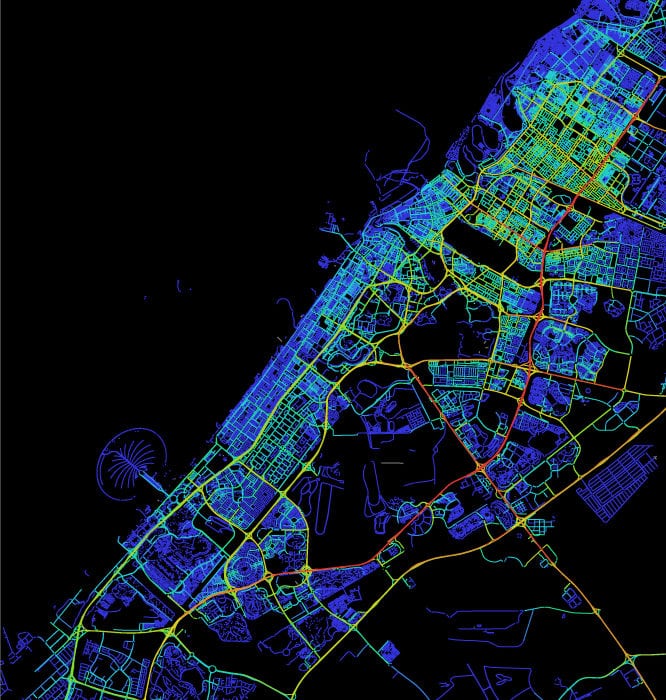
- Walk Score© for measuring the accessibility by foot to functions and services, in order to identify more lively neighborhoods where people have better chances of moving on foot
- Pedestrian Level Of Service (PLOS) for evaluating safety and comfort levels across the entire city, providing effective indications on priority of interventions
- Public Transport Accessibility Level (PTAL) for understanding the efficiency of connection with public transport network by taking into account the walking time to a public transport stop, the number and the frequency of services at that stop.
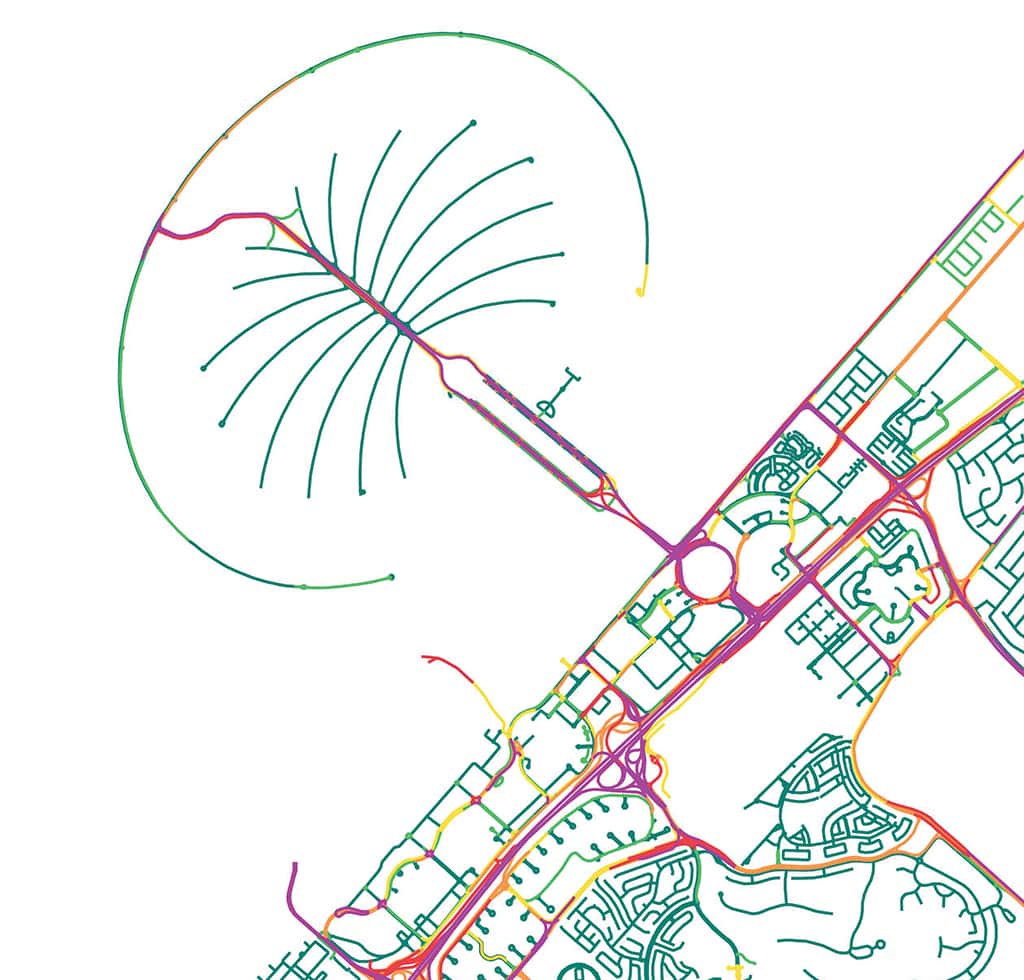
- Space Syntax for measuring the intuitiveness of the routes for pedestrians from origin to destination, in order to identify the streets and junctions with high pedestrian footfall
- CUBE by Citilabs for pedestrian simulation and modelling for replicating the current pedestrian flow patterns enabling the planners with a more informed design decisions especially for crowd management of major events.
Understand the streets
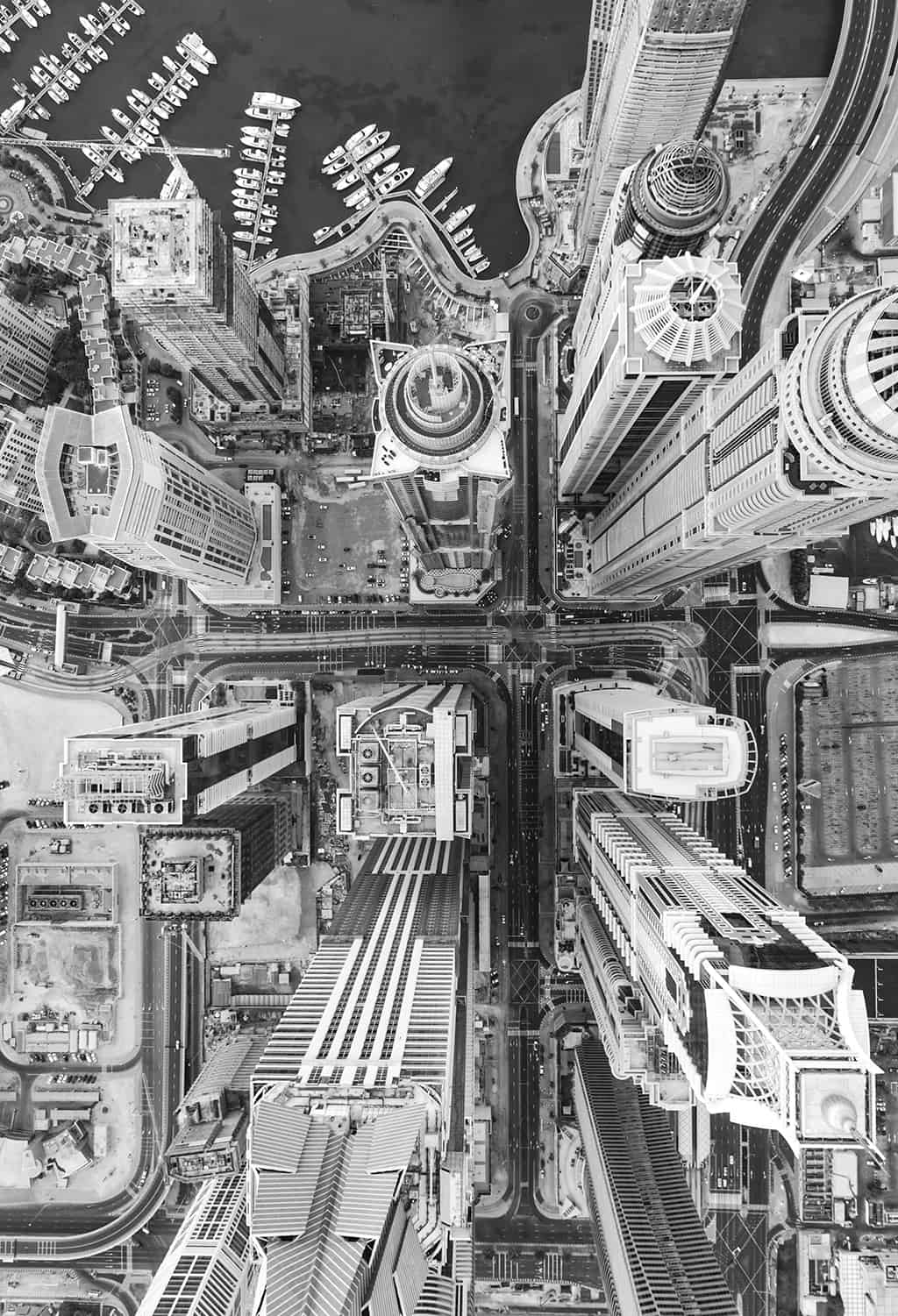
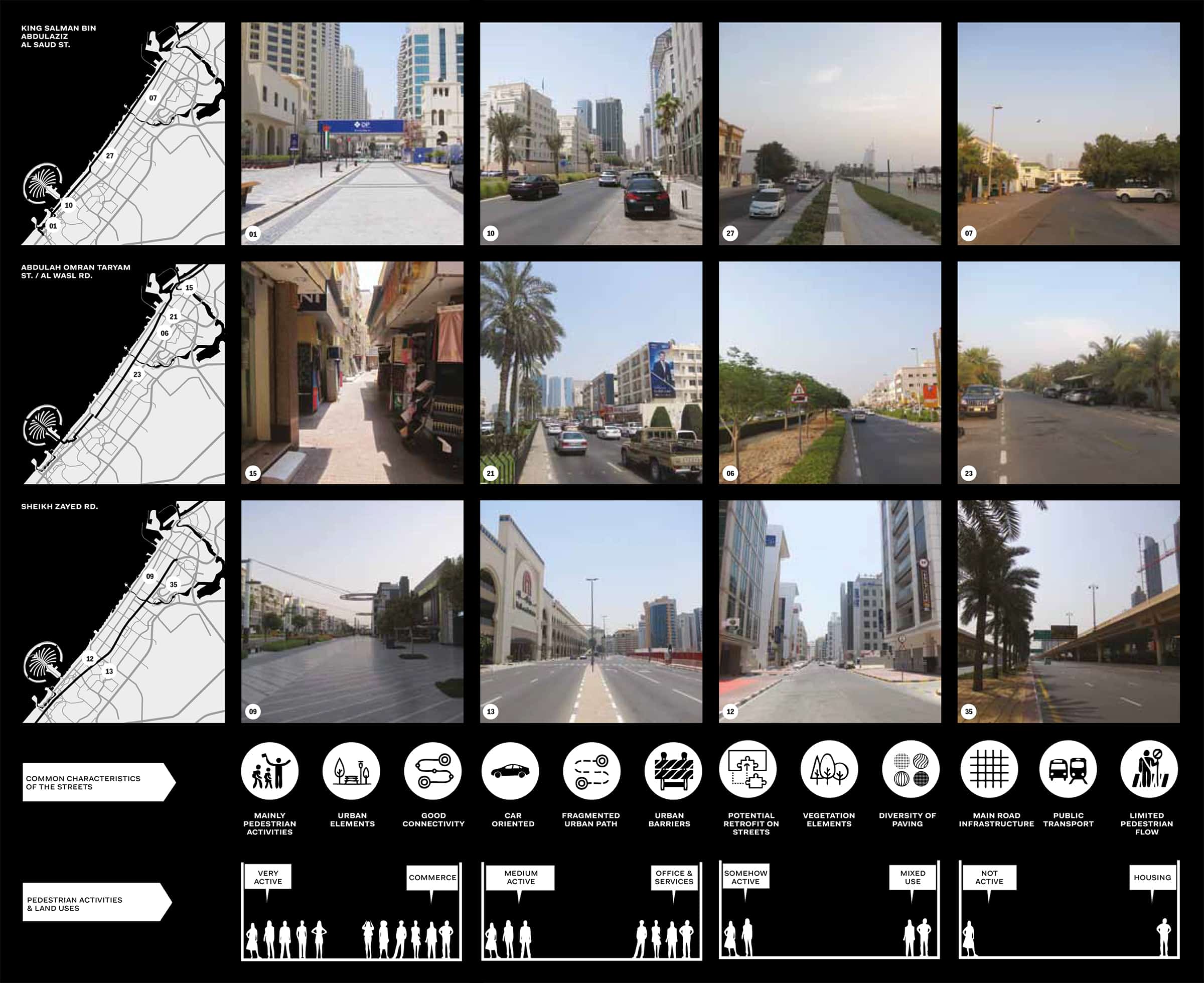
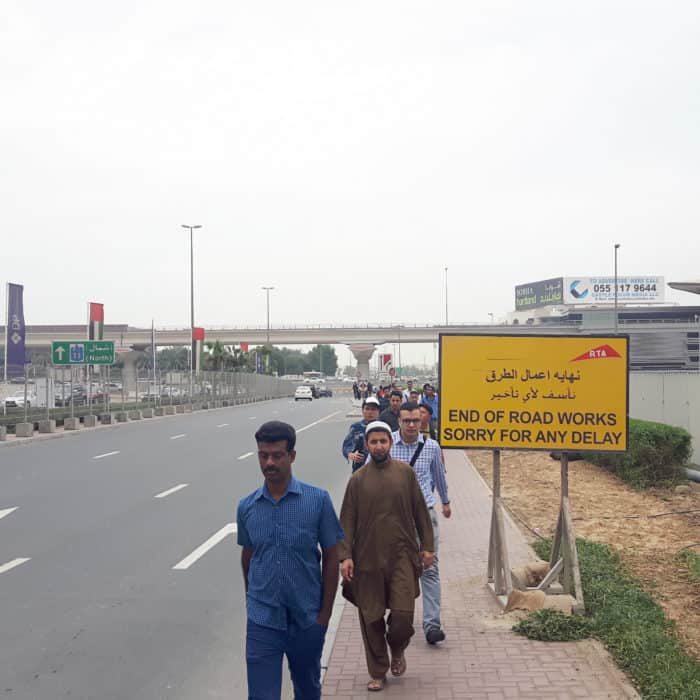
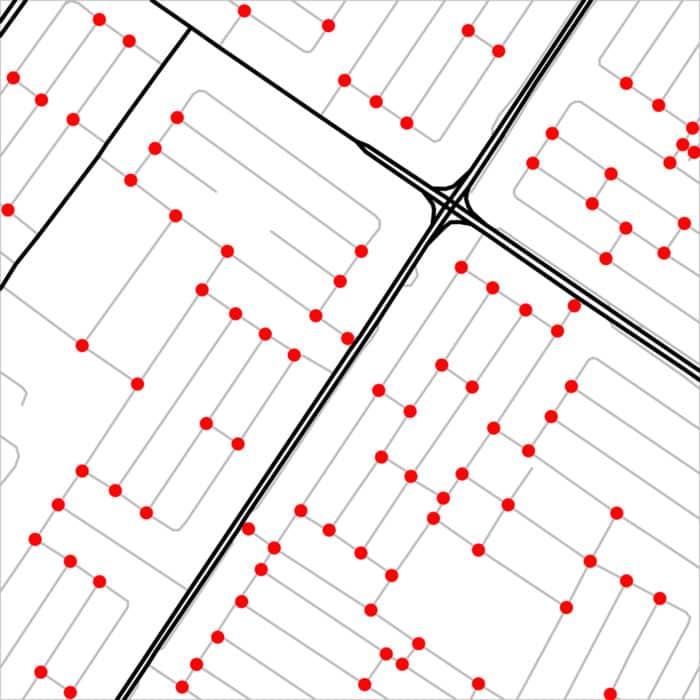
There is no straightforward way to describe the complexity of Dubai’s streets. From the narrowest alley in Deira to the widest boulevard, the streets and roads are dissected into their key features and smallest components, finding analogies and differences.
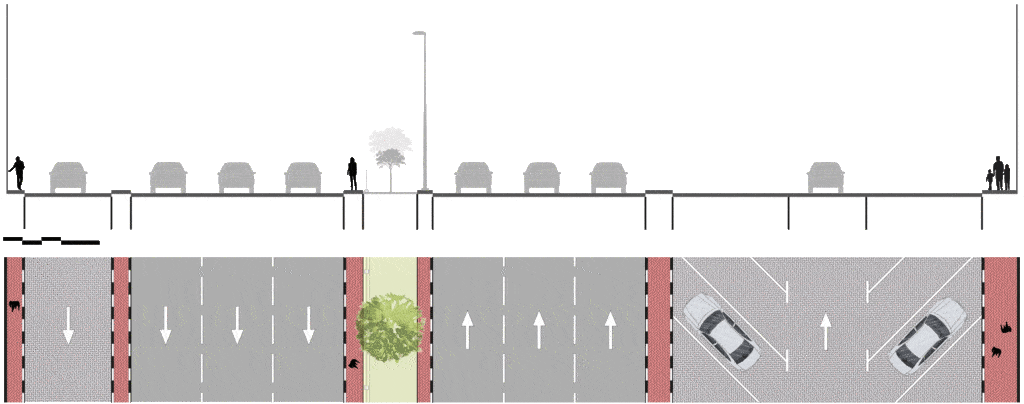
In addition, streets and roads of Dubai are dissected into their key features and smallest components for finding analogies and differences. These features includes junction’s typologies and spacing, measuring and allocation of street spaces, shading, greenery, bike lanes and facilities, pedestrian crossings, bus shelters, tram and so on.
Stitching the city: an Interview with Iyad Alsaka
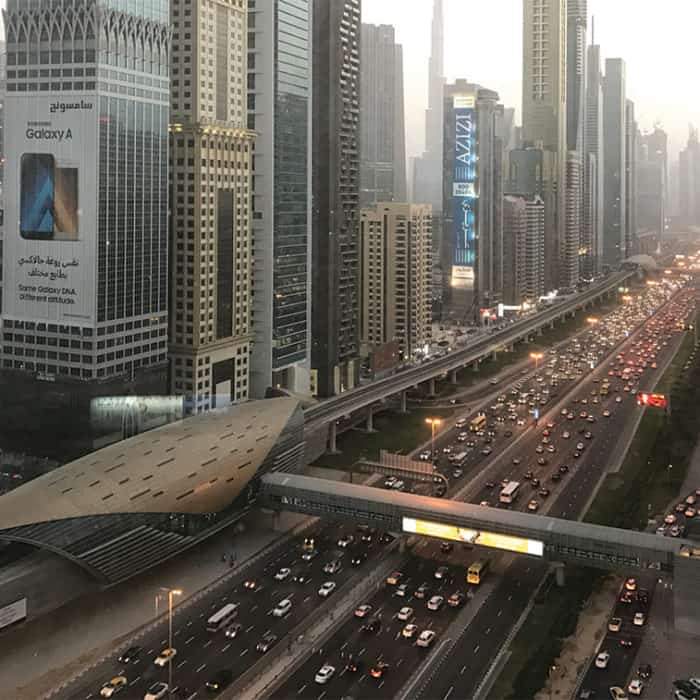
Sheikh Zayed Road
Junction Spacing: the case of Al Wasl Rd.
Allocation of space – Street space vs. Street proportions
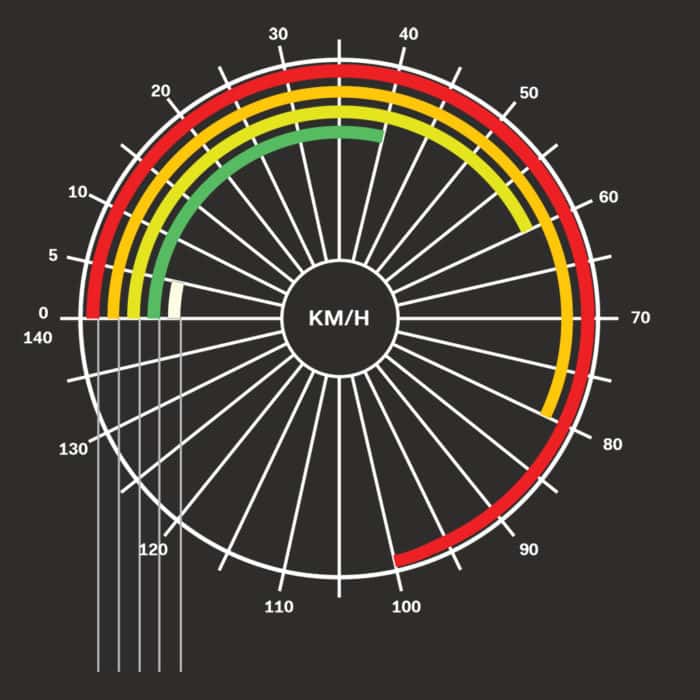
Tell me your speed and I will tell which street you are
Street Elements – Greenery
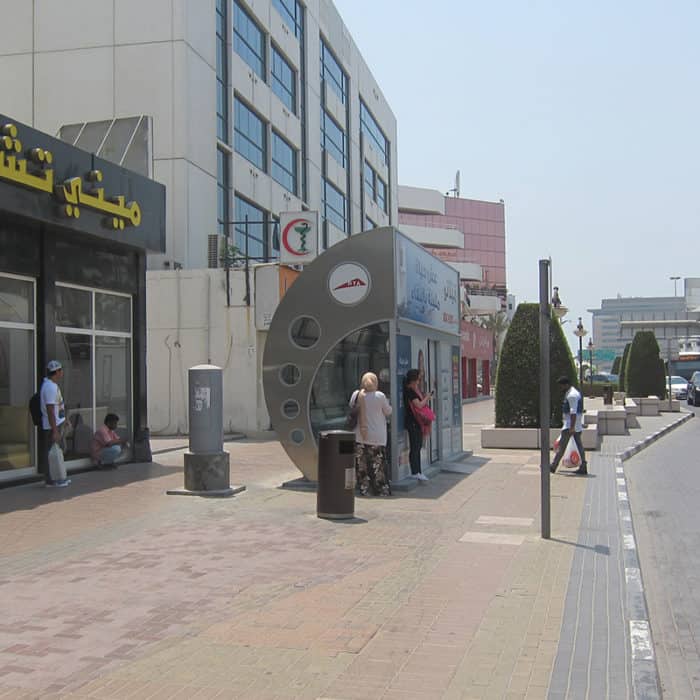
Air-conditioned bus stops: from shelters to service hubs
Retrofitting strategies
Strategy 01
Increase pedestrian safety and public realm quality by narrowing vehicular lanes